ZHCSFP4B November 2016 – June 2017 TMP468
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6
Register Maps
- 7.6.1
Register Information
- 7.6.1.1 Pointer Register
- 7.6.1.2 Local and Remote Temperature Value Registers
- 7.6.1.3 Software Reset Register
- 7.6.1.4 THERM Status Register
- 7.6.1.5 THERM2 Status Register
- 7.6.1.6 Remote Channel Open Status Register
- 7.6.1.7 Configuration Register
- 7.6.1.8 η-Factor Correction Register
- 7.6.1.9 Remote Temperature Offset Register
- 7.6.1.10 THERM Hysteresis Register
- 7.6.1.11 Local and Remote THERM and THERM2 Limit Registers
- 7.6.1.12 Block Read - Auto Increment Pointer
- 7.6.1.13 Lock Register
- 7.6.1.14 Manufacturer and Device Identification Plus Revision Registers
- 7.6.1
Register Information
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- RGT|16
订购信息
8 Application and Implementation
NOTE
Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validate and test their design implementation to confirm system functionality.
8.1 Application Information
The TMP468 device requires a transistor connected between the D+ and D– pins for remote temperature measurement. Tie the D+ pin to D– if the remote channel is not used and only the local temperature is measured. The SDA, ALERT, and THERM pins (and SCL, if driven by an open-drain output) require pullup resistors as part of the communication bus. TI recommends a 0.1-µF power-supply decoupling capacitor for local bypassing. Figure 22 and Figure 23 illustrate the typical configurations for the TMP468 device.
8.2 Typical Application
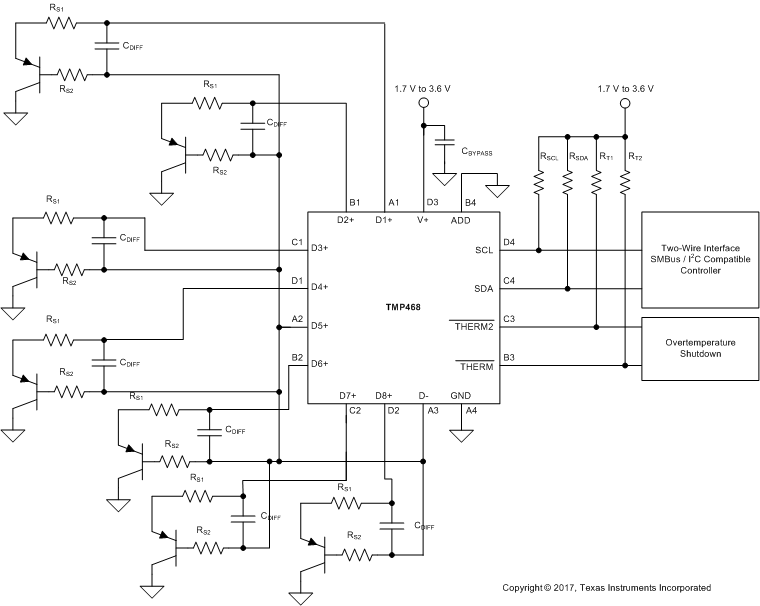
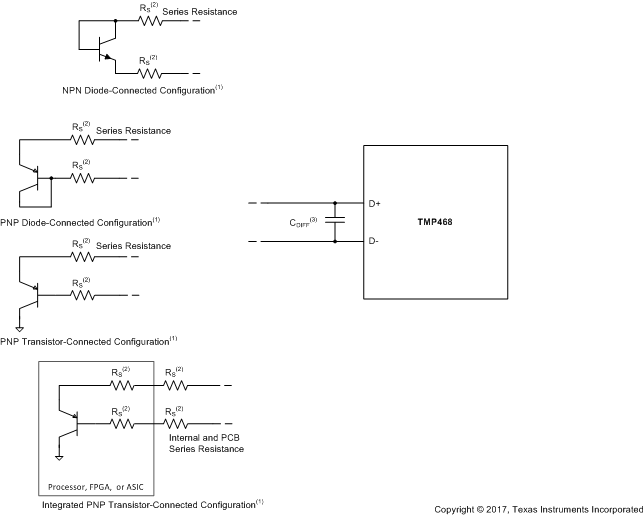 Figure 23. TMP468 Remote Transistor Configuration Options
Figure 23. TMP468 Remote Transistor Configuration Options
8.2.1 Design Requirements
The TMP468 device is designed to be used with either discrete transistors or substrate transistors built into processor chips, field programmable gate arrays (FPGAs), and application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) ; see Figure 23. Either NPN or PNP transistors can be used, as long as the base-emitter junction is used as the remote temperature sensor. NPN transistors must be diode-connected. PNP transistors can either be transistor- or diode-connected (see Figure 23).
Errors in remote temperature sensor readings are typically the consequence of the ideality factor (η-factor) and current excitation used by the TMP468 device versus the manufacturer-specified operating current for a given transistor. Some manufacturers specify a high-level and low-level current for the temperature-sensing substrate transistors. The TMP468 uses 7.5 μA (typical) for ILOW and 120 μA (typical) for IHIGH.
The ideality factor (η-factor) is a measured characteristic of a remote temperature sensor diode as compared to an ideal diode. The TMP468 allows for different η-factor values; see the η-Factor Correction Register section.
The η-factor for the TMP468 device is trimmed to 1.008. For transistors that have an ideality factor that does not match the TMP468 device, Equation 4 can be used to calculate the temperature error.
NOTE
For Equation 4 to be used correctly, the actual temperature (°C) must be converted to Kelvin (K).
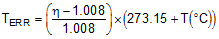
where
- TERR = error in the TMP468 device because η ≠ 1.008
- η = ideality factor of the remote temperature sensor
- T(°C) = actual temperature, and
In Equation 4, the degree of delta is the same for °C and K.
For η = 1.004 and T(°C) = 100°C:
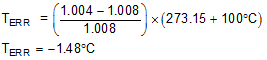
If a discrete transistor is used as the remote temperature sensor with the TMP468 device, then select the transistor according to the following criteria for best accuracy:
- Base-emitter voltage is > 0.25 V at 7.5 μA, at the highest-sensed temperature.
- Base-emitter voltage is < 0.95 V at 120 μA, at the lowest-sensed temperature.
- Base resistance is < 100 Ω.
- Tight control of VBE characteristics indicated by small variations in hFE (50 to 150).
Based on these criteria, TI recommends using a MMBT3904 (NPN) or a MMBT3906 (PNP) transistor.
8.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
The local temperature sensor inside the TMP468 is influenced by the ambient air around the device but mainly monitors the PCB temperature that it is mounted to. The thermal time constant for the TMP468 device is approximately two seconds. This constant implies that if the ambient air changes quickly by 100°C, then the TMP468 device takes approximately 10 seconds (that is, five thermal time constants) to settle to within 1°C of the final value. In most applications, the TMP468 package is in electrical (and therefore thermal) contact with the printed-circuit board (PCB), and subjected to forced airflow. The accuracy of the measured temperature directly depends on how accurately the PCB and forced airflow temperatures represent the temperature that the TMP468 device is measuring. Additionally, the internal power dissipation of the TMP468 device can cause the temperature to rise above the ambient or PCB temperature. The internal power is negligible because of the small current drawn by the TMP468 device. Equation 6 can be used to calculate the average conversion current for power dissipation and self-heating based on the number of conversions per second and temperature sensor channel enabled. Equation 7 shows an example with local and all remote sensor channels enabled and conversion rate of 1 conversion per second; see the Electrical Characteristics table for typical values required for these calculations. For a 3.3-V supply and a conversion rate of 1 conversion per second, the TMP468 device dissipates 0.224 mW (PDIQ = 3.3 V × 68 μA) when both the remote and local channels are enabled.
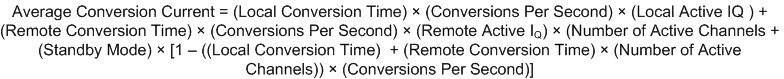
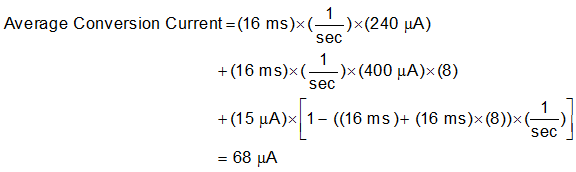
The temperature measurement accuracy of the TMP468 device depends on the remote and local temperature sensor being at the same temperature as the monitored system point. If the temperature sensor is not in good thermal contact with the part of the monitored system, then there is a delay between the sensor response and the system changing temperature. This delay is usually not a concern for remote temperature-sensing applications that use a substrate transistor (or a small, SOT-23 transistor) placed close to the monitored device.
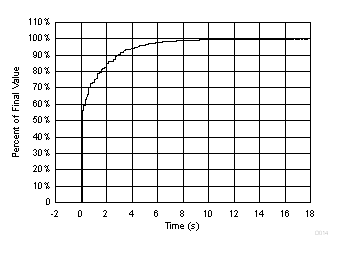
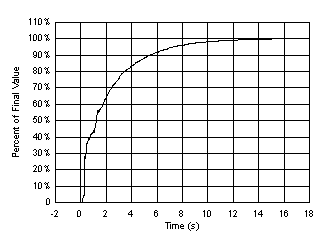
8.2.3 Application Curve
Figure 24 and Figure 25 show the typical step response to submerging a TMP468 device (initially at 25°C) in an oil bath with a temperature of 100°C and logging the local temperature readings.