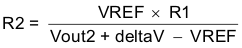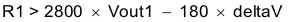ZHCS026C December 2010 – February 2016 TPS57060-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特征
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Fixed Frequency PWM Control
- 7.3.2 Slope Compensation Output Current
- 7.3.3 Low Dropout Operation and Bootstrap Voltage (BOOT)
- 7.3.4 Error Amplifier
- 7.3.5 Voltage Reference
- 7.3.6 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 7.3.7 Enable and Adjusting Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 7.3.8 Slow Start and Tracking Pin (SS/TR)
- 7.3.9 Overload Recovery Circuit
- 7.3.10 Constant Switching Frequency and Timing Resistor (RT/CLK Pin)
- 7.3.11 Overcurrent Protection and Frequency Shift
- 7.3.12 Selecting the Switching Frequency
- 7.3.13 How to Interface to RT/CLK Pin
- 7.3.14 Power Good (PWRGD Pin)
- 7.3.15 Overvoltage Transient Protection
- 7.3.16 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.3.17 Small Signal Model for Loop Response
- 7.3.18 Simple Small-Signal Model for Peak Current-Mode Control
- 7.3.19 Small Signal Model for Frequency Compensation
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Selecting the Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.2 Output Inductor Selection (LO)
- 8.2.2.3 Output Capacitor
- 8.2.2.4 Catch Diode
- 8.2.2.5 Input Capacitor
- 8.2.2.6 Slow Start Capacitor
- 8.2.2.7 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.8 Undervoltage Lockout Set Point
- 8.2.2.9 Output Voltage and Feedback Resistors Selection
- 8.2.2.10 Compensation
- 8.2.2.11 Discontinuous Mode and Eco Mode Boundary
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
订购信息
7.4.1 Sequencing
Many of the common power supply sequencing methods can be implemented using the SS/TR, EN and PWRGD pins. The sequential method can be implemented using an open drain output of a power on reset pin of another device. The sequential method is illustrated in Figure 42 using two TPS57060-Q1 devices. The power good is coupled to the EN pin on the TPS57060-Q1 device which enables the second power supply when the primary supply reaches regulation. If needed, a 1nF ceramic capacitor on the EN pin of the second power supply provides a 1-ms start-up delay. Figure 43 shows the results of Figure 42.
Figure 44 shows a method for ratiometric start-up sequence by connecting the SS/TR pins together. The regulator outputs will ramp up and reach regulation at the same time. When calculating the slow start time the pullup current source must be doubled in Equation 6. Figure 45 shows the results of Figure 44.
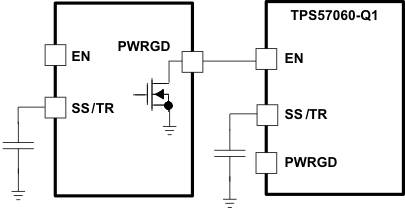 Figure 42. Schematic for Sequential Start-Up Sequence
Figure 42. Schematic for Sequential Start-Up Sequence Figure 43. Sequential Startup Using EN and PWRGD
Figure 43. Sequential Startup Using EN and PWRGD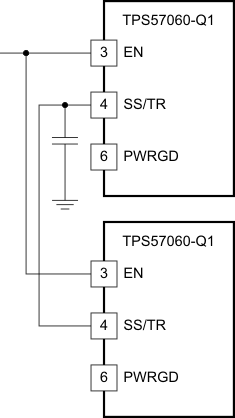 Figure 44. Schematic for Ratiometric Start-Up Using Coupled SS/TR Pins
Figure 44. Schematic for Ratiometric Start-Up Using Coupled SS/TR Pins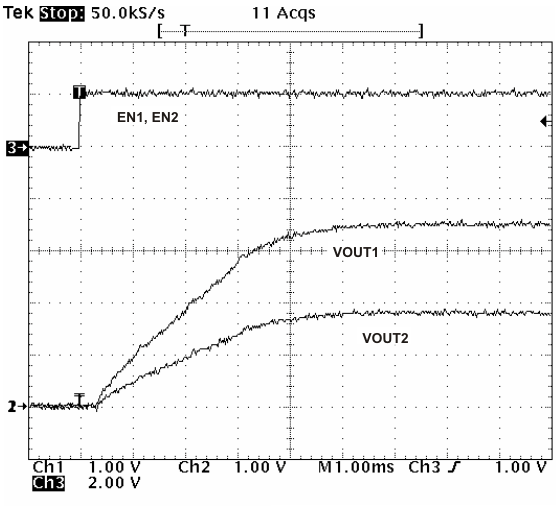 Figure 45. Ratiometric Startup Using Coupled SS/TR pins
Figure 45. Ratiometric Startup Using Coupled SS/TR pins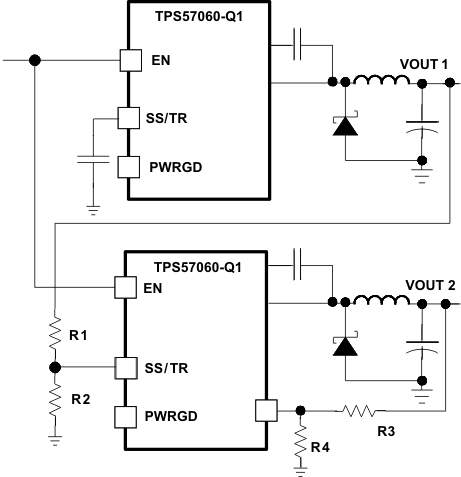 Figure 46. Schematic for Ratiometric and Simultaneous Start-Up Sequence
Figure 46. Schematic for Ratiometric and Simultaneous Start-Up SequenceRatiometric and simultaneous power supply sequencing can be implemented by connecting the resistor network of R1 and R2 shown in Figure 46 to the output of the power supply that needs to be tracked or another voltage reference source. Using Equation 24 and Equation 25, the tracking resistors can be calculated to initiate the Vout2 slightly before, after or at the same time as Vout1. Equation 26 is the voltage difference between Vout1 and Vout2 at the 95% of nominal output regulation.
The deltaV variable is 0 V for simultaneous sequencing. To minimize the effect of the inherent SS/TR to VSENSE offset (Vssoffset) in the slow start circuit and the offset created by the pullup current source (Iss) and tracking resistors, the Vssoffset and Iss are included as variables in the equations.
To design a ratiometric start up in which the Vout2 voltage is slightly greater than the Vout1 voltage when Vout2 reaches regulation, use a negative number in Equation 24 through Equation 26 for deltaV. Equation 26 results in a positive number for applications which the Vout2 is slightly lower than Vout1 when Vout2 regulation is achieved.
Because the SS/TR pin must be pulled below 40 mV before starting after an EN, UVLO or thermal shutdown fault, careful selection of the tracking resistors is needed to ensure the device will restart after a fault. Make sure the calculated R1 value from Equation 24 is greater than the value calculated in Equation 27 to ensure the device can recover from a fault.
As the SS/TR voltage becomes more than 85% of the nominal reference voltage the Vssoffset becomes larger as the slow start circuits gradually handoff the regulation reference to the internal voltage reference. The SS/TR pin voltage needs to be greater than 1.3 V for a complete handoff to the internal voltage reference as shown in Figure 23.