SBAS654G June 2014 – January 2020
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Power Ratings
- 7.6 Insulation Specifications
- 7.7 Safety-Related Certifications
- 7.8 Safety Limiting Values
- 7.9 Electrical Characteristics: AMC1305M05
- 7.10 Electrical Characteristics: AMC1305x25
- 7.11 Switching Characteristics
- 7.12 Insulation Characteristics Curves
- 7.13 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.3.3 Digital Output
A differential input signal of 0 V ideally produces a stream of ones and zeros that are high 50% of the time. A differential input of 250 mV (for the AMC1305x25) or 50 mV (for the AMC1305M05) produces a stream of ones and zeros that are high 90% of the time. A differential input of –250 mV (–50 mV for the AMC1305M05) produces a stream of ones and zeros that are high 10% of the time. These input voltages are also the specified linear ranges of the different AMC1305 versions with performance as specified in this document. If the input voltage value exceeds these ranges, the output of the modulator shows non-linear behavior while the quantization noise increases. The output of the modulator would clip with a stream of only zeros with an input less than or equal to –312.5 mV (–62.5 mV for the AMC1305M05) or with a stream of only ones with an input greater than or equal to 312.5 mV (62.5 mV for the AMC1305M05). In this case, however, the AMC1305 generates a single 1 (if the input is at negative full-scale) or 0 every 128 clock cycles to indicate proper device function (see the Fail-Safe Output section for more details). The input voltage versus the output modulator signal is shown in Figure 50.
The density of ones in the output bit-stream for any input voltage value (with the exception of a full-scale input signal as described in Output Behavior in Case of Full-Scale Input) can be calculated using Equation 1:
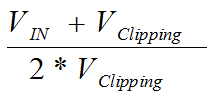
The AMC1305 system clock is typically 20 MHz and is provided externally at the CLKIN pin. Data are synchronously provided at 20 MHz at the DOUT pin. Data change at the CLKIN falling edge. For more details, see the Switching Characteristics table.
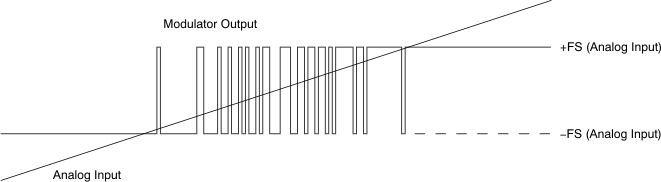 Figure 50. Analog Input versus AMC1305 Modulator Output
Figure 50. Analog Input versus AMC1305 Modulator Output