SLASEB7D June 2017 – December 2020
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Functional Block Diagrams
- 5 Revision History
- 6 Device Comparison
- 7 Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
8 Specifications
- 8.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 8.2 ESD Ratings
- 8.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 8.4 Active Mode Supply Current Into VCC Excluding External Current
- 8.5 Typical Characteristics, Active Mode Supply Currents
- 8.6 Low-Power Mode (LPM0, LPM1) Supply Currents Into VCC Excluding External Current
- 8.7 Low-Power Mode (LPM2, LPM3, LPM4) Supply Currents (Into VCC) Excluding External Current
- 8.8 Low-Power Mode With LCD Supply Currents (Into VCC) Excluding External Current
- 8.9 Low-Power Mode (LPMx.5) Supply Currents (Into VCC) Excluding External Current
- 8.10 Typical Characteristics, Low-Power Mode Supply Currents
- 8.11 Typical Characteristics, Current Consumption per Module (1)
- 8.12 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for 100-Pin LQFP (PZ) Package
- 8.13
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 8.13.1 Power Supply Sequencing
- 8.13.2 Reset Timing
- 8.13.3 Clock Specifications
- 8.13.4 Wake-up Characteristics
- 8.13.5 Digital I/Os
- 8.13.6 LEA
- 8.13.7 Timer_A and Timer_B
- 8.13.8
eUSCI
- 8.13.8.1 eUSCI (UART Mode) Clock Frequency
- 8.13.8.2 eUSCI (UART Mode) Switching Characteristics
- 8.13.8.3 eUSCI (SPI Master Mode) Clock Frequency
- 8.13.8.4 eUSCI (SPI Master Mode) Switching Characteristics
- 8.13.8.5 eUSCI (SPI Master Mode) Timing Diagrams
- 8.13.8.6 eUSCI (SPI Slave Mode) Switching Characteristics
- 8.13.8.7 eUSCI (SPI Slave Mode) Timing Diagrams
- 8.13.8.8 eUSCI (I2C Mode) Switching Characteristics
- 8.13.8.9 eUSCI (SPI Slave Mode) Timing Diagrams
- 8.13.9 Segment LCD Controller
- 8.13.10
ADC12_B
- 8.13.10.1 12-Bit ADC, Power Supply and Input Range Conditions
- 8.13.10.2 12-Bit ADC, Timing Parameters
- 8.13.10.3 12-Bit ADC, Linearity Parameters
- 8.13.10.4 12-Bit ADC, Dynamic Performance With External Reference
- 8.13.10.5 12-Bit ADC, Dynamic Performance With Internal Reference
- 8.13.10.6 12-Bit ADC, Temperature Sensor and Built-In V1/2
- 8.13.10.7 12-Bit ADC, External Reference
- 8.13.10.8 Temperature Sensor Typical Characteristics
- 8.13.11 Reference
- 8.13.12 Comparator
- 8.13.13 FRAM
- 8.13.14 USS
- 8.13.15 Emulation and Debug
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 CPU
- 9.3 Ultrasonic Sensing Solution (USS) Module
- 9.4 Low-Energy Accelerator (LEA) for Signal Processing
- 9.5 Operating Modes
- 9.6 Interrupt Vector Table and Signatures
- 9.7 Bootloader (BSL)
- 9.8 JTAG Operation
- 9.9 FRAM Controller A (FRCTL_A)
- 9.10 RAM
- 9.11 Tiny RAM
- 9.12 Memory Protection Unit (MPU) Including IP Encapsulation
- 9.13
Peripherals
- 9.13.1 Digital I/O
- 9.13.2 Oscillator and Clock System (CS)
- 9.13.3 Power-Management Module (PMM)
- 9.13.4 Hardware Multiplier (MPY)
- 9.13.5 Real-Time Clock (RTC_C)
- 9.13.6 Measurement Test Interface (MTIF)
- 9.13.7 Watchdog Timer (WDT_A)
- 9.13.8 System Module (SYS)
- 9.13.9 DMA Controller
- 9.13.10 Enhanced Universal Serial Communication Interface (eUSCI)
- 9.13.11 TA0, TA1, and TA4
- 9.13.12 TA2 and TA3
- 9.13.13 TB0
- 9.13.14 ADC12_B
- 9.13.15 USS
- 9.13.16 Comparator_E
- 9.13.17 CRC16
- 9.13.18 CRC32
- 9.13.19 AES256 Accelerator
- 9.13.20 True Random Seed
- 9.13.21 Shared Reference (REF)
- 9.13.22 LCD_C
- 9.13.23 Embedded Emulation
- 9.14
Input/Output Diagrams
- 9.14.1 Port Function Select Registers (PySEL1 , PySEL0)
- 9.14.2 Port P1 (P1.0 and P1.1) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.3 Port P1 (P1.2 to P1.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.4 Port P2 (P2.0 to P2.3) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.5 Port P2 (P2.4 to P2.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.6 Port P3 (P3.0 to P3.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.7 Port P4 (P4.0 to P4.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.8 Port P5 (P5.0 to P5.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.9 Port P6 (P6.0) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.10 Port P6 (P6.1 to P6.5) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.11 Port P6 (P6.6 and P6.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.12 Port P7 (P7.0 to P7.3) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.13 Port P7 (P7.4) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.14 Port P7 (P7.5) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.15 Port P7 (P7.6 and P7.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.16 Port P8 (P8.0 to P8.3) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.17 Port P8 (P8.4 to P8.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.18 Port P9 (P9.0 to P9.3) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.19 Port PJ (PJ.0 to PJ.3) JTAG Pins TDO, TMS, TCK, TDI/TCLK, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.20 Port PJ (PJ.4 and PJ.5) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.21 Port PJ (PJ.6 and PJ.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.15 Device Descriptors (TLV)
- 9.16 Memory Map
- 9.17 Identification
-
10Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 10.1
Device Connection and Layout Fundamentals
- 10.1.1 Power Supply Decoupling and Bulk Capacitors
- 10.1.2 External Oscillator (HFXT and LFXT)
- 10.1.3 USS Oscillator (USSXT)
- 10.1.4 Transducer Connection to the USS Module
- 10.1.5 Charge Pump Control of Input Multiplexer
- 10.1.6 JTAG
- 10.1.7 Reset
- 10.1.8 Unused Pins
- 10.1.9 General Layout Recommendations
- 10.1.10 Do's and Don'ts
- 10.2 Peripheral- and Interface-Specific Design Information
- 10.1
Device Connection and Layout Fundamentals
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.14.2 Port P1 (P1.0 and P1.1) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
Figure 9-3 shows the port diagram. Table 9-25 summarizes the selection of the pin function.
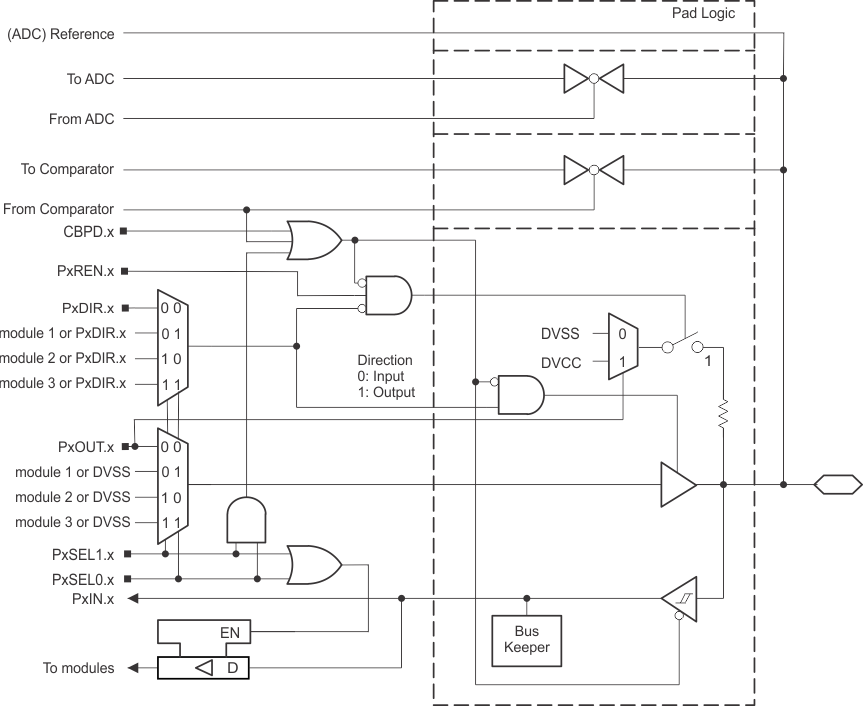
Functional representation only.
Figure 9-3 Port P1 (P1.0 to P1.1) DiagramTable 9-25 Port P1 (P1.0 to P1.1) Pin Functions
| PIN NAME (P1.x) | x | FUNCTION | CONTROL BITS AND SIGNALS(1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1DIR.x | P1SEL1.x | P1SEL0.x | |||
| P1.0/UCA1CLK/TA1.0/A0/C0/ VREF-/VeREF- | 0 | P1.0 (I/O) | 0 = Input, 1 = Output | 0 | 0 |
| UCA1CLK | X(4) | 0 | 1 | ||
| TA1.CCI0A | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| TA1.0 | 1 | ||||
| A0, C0, VREF-, VeREF-(2)(3) | X | 1 | 1 | ||
| P1.1/UCA1STE/TA4.0/A1/C1/ VREF+/VeREF+ | 1 | P1.1 (I/O) | 0 = Input, 1 = Output | 0 | 0 |
| UCA1STE | X(4) | 0 | 1 | ||
| TA4.CCI0A | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| TA4.0 | 1 | ||||
| A1, C1, VREF+, VeREF+(2)(3) | X | 1 | 1 | ||
(1) X = Don't care
(2) Setting P1SEL1.x and P1SEL0.x disables the output driver and the input Schmitt trigger to prevent parasitic cross currents when applying analog signals.
(3) Setting the CEPDx bit of the comparator disables the output driver and the input Schmitt trigger to prevent parasitic cross currents when applying analog signals. Selecting the Cx input pin to the comparator multiplexer with the input select bits in the comparator module automatically disables output driver and input buffer for that pin, regardless of the state of the associated CEPDx bit.
(4) Direction controlled by eUSCI_A1 module.