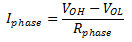SLVA767A September 2016 – December 2016 SN75469 , TPL7407L , TPL9201 , ULN2003A , ULN2003B , ULN2003V12 , ULN2004A , ULQ2003A , ULQ2003A-Q1 , ULQ2004A , ULQ2004A-Q1
3.4 Detailed Design Considerations
When using a peripheral driver for stepper motor driving applications there are a few design considerations that should be highlighted.
- VCC1 and VCC2 should be within the acceptable recommended voltage range - see device Electrical Characteristics for further information.
- Logic Inputs should be within the acceptable recommended voltage range - see device Electrical Characteristics for further information.
- The current through each motor phase (Iphase) is a function of the high-level output voltage (VOH), the low-level output voltage (VOL) and the phase resistance (Rphase)
- Equation 2 provides the equation for the Relay Current
- See device Electrical Characteristics for the maximum allowable continuous output current per channel (IO), high-level output voltage (VOH), and low-level output voltage (VOL)
Equation 2.