SLVA787 September 2016 LM8330 , LM8335 , P82B715 , P82B96 , PCA6107 , PCA9306 , PCA9306-Q1 , PCA9515A , PCA9515B , PCA9518 , PCA9534 , PCA9534A , PCA9535 , PCA9536 , PCA9538 , PCA9539 , PCA9543A , PCA9544A , PCA9545A , PCA9546A , PCA9548A , PCA9554 , PCA9554A , PCA9555 , PCA9557 , PCF8574 , PCF8574A , PCF8575 , PCF8575C , TCA4311A , TCA6408A , TCA6416A , TCA6418E , TCA6424A , TCA9509 , TCA9517 , TCA9517A , TCA9534 , TCA9534A , TCA9535 , TCA9538 , TCA9539 , TCA9539-Q1 , TCA9543A , TCA9544A , TCA9545A , TCA9546A , TCA9548A , TCA9554 , TCA9554A , TCA9555 , TCA9617A , TCA9617B , TCA9800 , TCA9801 , TCA9802 , TCA9803
4.1.1 Static Voltage Offset
Certain devices within the I2C buffer/repeater portfolio, such as TCA9517/A and TCA9617/A/B, contain a static voltage offset. The type of buffer design on the B-side prevents these devices from being used in series with devices that use a static voltage offset. When a static voltage offset is present on the B-side of these TCA devices, they will be unable to recognize buffered low signals as a valid low and do not propagate it as a buffered low again. An example of this would include, taking two TCA9517A devices and placing them in an A-B B-A configuration. By having both B-sides in series, the design runs the risk of miscommunicating low signals as the device will be unable to recognize this and result in transmitting a high.
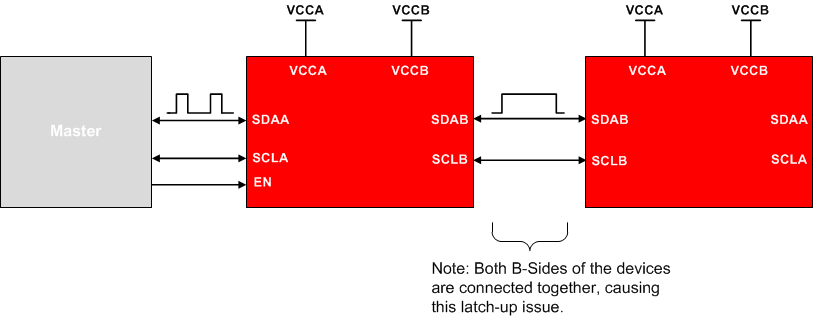 Figure 9. Example of B-B side mismatch configuration for I2C buffers
Figure 9. Example of B-B side mismatch configuration for I2C buffers