SLVAE22A July 2018 – March 2019 TPS54334 , TPS65251 , TPS65251-1 , TPS65251-2 , TPS65251-3 , TPS652510 , TPS65261 , TPS65263 , TPS65263-1Q1 , TPS65263-Q1 , TPS65265 , TPS65266 , TPS65266-1 , TPS65270 , TPS65273V , TPS65276V , TPS65279 , TPS65279V
3.1 Simplified Small Signal Model for Power Stage Gain
Ignoring the inductor current ripple, the load current (iLoad) is equal to the inductor current (iL) in CCM. Figure 2 shows a simplified whole system small signal model.
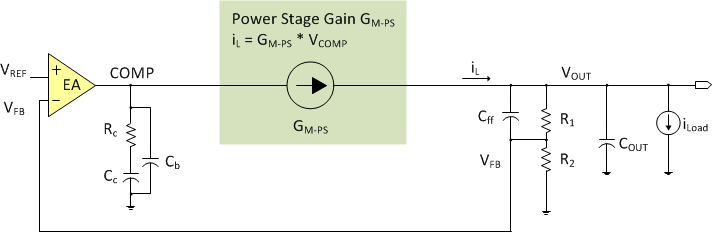 Figure 2. Simplified Small Signal Model for PCM BUCK Converter
Figure 2. Simplified Small Signal Model for PCM BUCK Converter Equation 2 calculates the AC small signal relationship between VCOMP and iLoad.
Equation 2. 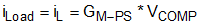
Equation 3 expresses the GM-PS.
Equation 3. 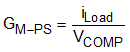
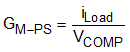
They are the small signal differential data where VCOMP and iLOAD are not the directly measured data.