SLVAEW6 December 2020 TPS2661
- Trademarks
- 1Introduction
- 2Protection Required for Current Inputs in Analog Input Modules
- 3Typical Discrete Circuit for Protection of Current Input
-
4TPS26610 for Analog Current Loop
Protection
- 4.1 Current Input Protection with TPS26610
- 4.2 Accurate Current Limiting with TPS26610
- 4.3 Leakage Current of TPS26610 and Current Measurement Accuracy
- 4.4 Protection from Mis-wiring to Field Power Supplies
- 4.5 Heating and Temperature Rise with TPS26610
- 4.6 Reduction in PCB Size with TPS26610 for Current Input Protection
- 5Conclusion
3.2 Heating and Temperature Rise with Discrete Circuit
As the PTC and Zener diode don’t provide the cut-off protection during miswiring faults, there is a continuous flow of current through the burden resistor, PTC, and Zener diodes. This current flow leads to power dissipation in these components and heating of the entire module. Figure 3-7 provides the temperature rise in PTC during miswiring faults. The temperature of PTC rises ~95°C above ambient temperature during miswiring faults
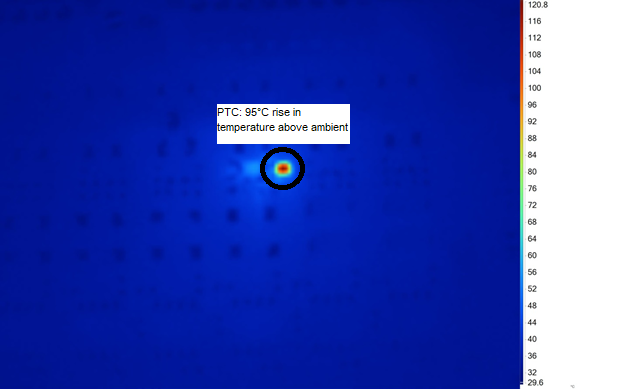 Figure 3-7 Temperature rise with Discrete
Circuit
Figure 3-7 Temperature rise with Discrete
Circuit