SLVSD76C February 2016 – July 2017
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8 Detailed Description
8.1 Overview
The TPS22918 is a 5.5-V, 2-A load switch in a 6-pin SOT-23 package. To reduce voltage drop for low voltage and high current rails, the device implements a low resistance N-channel MOSFET which reduces the drop out voltage across the device.
The device has a configurable slew rate which helps reduce or eliminate power supply droop because of large inrush currents. Furthermore, the device features a QOD pin, which allows the configuration of the discharge rate of VOUT once the switch is disabled. During shutdown, the device has very low leakage currents, thereby reducing unnecessary leakages for downstream modules during standby. Integrated control logic, driver, charge pump, and output discharge FET eliminates the need for any external components which reduces solution size and bill of materials (BOM) count.
8.2 Functional Block Diagram
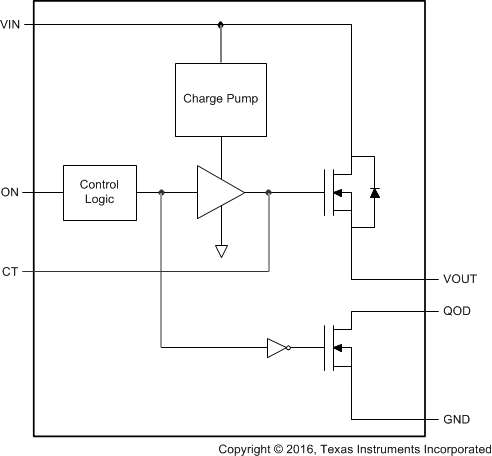
8.3 Feature Description
8.3.1 On and Off Control
The ON pin controls the state of the switch. ON is active high and has a low threshold, making it capable of interfacing with low-voltage signals. The ON pin is compatible with standard GPIO logic threshold. It can be used with any microcontroller with 1 V or higher GPIO voltage. This pin cannot be left floating and must be driven either high or low for proper functionality.
8.3.2 Quick Output Discharge (QOD)
The TPS22918 includes a QOD feature. The QOD pin can be configured in one of three ways:
- QOD pin shorted to VOUT pin. Using this method, the discharge rate after the switch becomes disabled is controlled with the value of the internal resistance RPD. The value of this resistance is listed in the Electrical Characteristics table.
- QOD pin connected to VOUT pin using an external resistor REXT. After the switch becomes disabled, the discharge rate is controlled by the value of the total resistance of the QOD. To adjust the total QOD resistance, Equation 1 can be used:
- RQOD = Total output discharge resistance
- RPD = Internal pulldown resistance
- REXT = External resistance placed between the VOUT and QOD pin.
- QOD pin is unused and left floating. Using this method, there will be no quick output discharge functionality, and the output will remain floating after the switch is disabled.
where
The fall times of the device depend on many factors including the total resistance of the QOD, VIN, and the output capacitance. When QOD is shorted to VOUT, the fall time will change over VIN as the internal RPD varies over VIN. To calculate the approximate fall time of VOUT for a given RQOD, use Equation 2 and Table 1.
where
- VCAP = Voltage across the capacitor (V)
- t = Time since power supply removal (s)
- τ = Time constant equal to RQOD × CL
The fall times' dependency on VIN becomes minimal as the QOD value increases with additional external resistance. See Table 1 for QOD fall times.
Table 1. QOD Fall Times
| VIN (V) | (1)FALL TIME (μs) 90% - 10%, CIN = 1 μF, IOUT = 0 A , VON = 0 V |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TA = 25°C | TA = 85°C | |||||
| CL = 1 μF | CL = 10 μF | CL = 100 μF | CL = 1 μF | CL = 10 μF | CL = 100 μF | |
| 5.5 | 42 | 190 | 1880 | 40 | 210 | 2150 |
| 5 | 43 | 200 | 1905 | 45 | 220 | 2200 |
| 3.3 | 47 | 230 | 2150 | 50 | 260 | 2515 |
| 2.5 | 58 | 300 | 2790 | 60 | 345 | 3290 |
| 1.8 | 75 | 430 | 4165 | 80 | 490 | 4950 |
| 1.2 | 135 | 955 | 9910 | 135 | 1035 | 10980 |
| 1 | 230 | 1830 | 19625 | 210 | 1800 | 19270 |
8.3.2.1 QOD when System Power is Removed
The adjustable QOD can be used to control the power down sequencing of a system even when the system power supply is removed. When the power is removed, the input capacitor discharges at VIN. Past a certain VIN level, the strength of the RPD will be reduced. If there is still remaining charge on the output capacitor, this will result in longer fall times. For further information regarding this condition, see the Shutdown Sequencing During Unexpected System Power Loss section.
8.3.2.2 Internal QOD Considerations
Special considerations must be taken when using the internal RPD by shorting the QOD pin to the VOUT pin. The internal RPD is a pulldown resistance designed to quickly discharge a load after the switch has been disabled. Care must be used to ensure that excessive current does not flow through RPD during discharge so that the maximum TJ of 125°C is not exceeded. When using only the internal RPD to discharge a load, the total capacitive load must not exceed 200 µF. Otherwise, an external resistor, REXT, must be used to ensure the amount of current flowing through RPD is properly limited and the maximum TJ is not exceeded. To ensure the device is not damaged, the remaining charge from CL must decay naturally through the internal QOD resistance and should not be driven.
8.3.3 Adjustable Rise Time (CT)
A capacitor to GND on the CT pin sets the slew rate of VOUT. The CT capacitor will charge up until shortly after the switch is turned on and VOUT becomes stable. Once VOUT become stable, the capactior will discharge to ground. An approximate formula for the relationship between CT and the slew rate is shown in Equation 3:
where
- SR = slew rate (in µs/V)
- CT = the capacitance value on the CT pin (in pF)
- The units for the constant 30 are µs/V. The units for the constant 0.55 are µs/(V × pF).
This equation accounts for 10% to 90% measurement on VOUT and does not apply for CT = 0 pF. Use Table 2 to determine rise times for when CT = 0 pF.
Rise time can be calculated by multiplying the input voltage by the slew rate. Table 2 contains rise time values measured on a typical device.
Table 2. Rise Time Table
| CT× (pF) | RISE TIME (µs) 10% - 90%, CL = 0.1 µF, CIN = 1 µF, RL = 10 Ω
(1) |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIN = 5 V | VN = 3.3 V | VIN = 2.5 V | VIN = 1.8 V | VIN = 1.5 V | VIN = 1.2 V | VIN = 1 V | |
| 0 | 135 | 95 | 75 | 60 | 50 | 45 | 40 |
| 220 | 650 | 455 | 350 | 260 | 220 | 185 | 160 |
| 470 | 1260 | 850 | 655 | 480 | 415 | 340 | 300 |
| 1000 | 2540 | 1680 | 1300 | 960 | 810 | 660 | 560 |
| 2200 | 5435 | 3580 | 2760 | 2020 | 1715 | 1390 | 1220 |
| 4700 | 12050 | 7980 | 6135 | 4485 | 3790 | 3120 | 2735 |
| 10000 | 26550 | 17505 | 13460 | 9790 | 8320 | 6815 | 5950 |
As the voltage across the capacitor approaches the capacitor rated voltage, the effective capacitance reduces. Depending on the dielectric material used, the voltage coefficient changes. See Table 3 for the recommended minimum voltage rating for the CT capacitor. If using VIN = 1.2 V or 4 V, it is recommended to use the higher of the two CT Voltage ratings specified.
Table 3. Recommended CT Capacitor Voltage Rating
| VIN (V) | RECOMMENDED CT CAPACITOR VOLTAGE RATING (V) |
|---|---|
| 1 V to 1.2 V | 10 |
| 1.2 V to 4 V | 16 |
| 4 V to 5.5 V | 20 |
8.4 Device Functional Modes
Table 4 describes the connection of the VOUT pin depending on the state of the ON pin.
Table 4. VOUT Connection
| ON | QOD CONFIGURATION | TPS22918 VOUT |
|---|---|---|
| L | QOD pin connected to VOUT with REXT | GND (via REXT+RPD) |
| L | QOD pin tied to VOUT directly | GND (via RPD) |
| L | QOD pin left open | Open |
| H | Any valid QOD configuration | VIN |