ZHCSL68C April 2017 – December 2020 TPS7A84A
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics: General
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics: TPS7A8400A
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics: TPS7A8401A
- 6.8 Typical Characteristics: TPS7A8400A
- 6.9 Typical Characteristics: TPS7A8401A
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1
Application Information
- 8.1.1
External Component Selection
- 8.1.1.1 Adjustable Operation
- 8.1.1.2 ANY-OUT Programmable Output Voltage
- 8.1.1.3 ANY-OUT Operation
- 8.1.1.4 Increasing ANY-OUT Resolution for LILO Conditions
- 8.1.1.5 Current Sharing
- 8.1.1.6 Recommended Capacitor Types
- 8.1.1.7 Input and Output Capacitor Requirements (CIN and COUT)
- 8.1.1.8 Feed-Forward Capacitor (CFF)
- 8.1.1.9 Noise-Reduction and Soft-Start Capacitor (CNR/SS)
- 8.1.2 Start-Up
- 8.1.3 AC and Transient Performance
- 8.1.4 DC Performance
- 8.1.5 Sequencing Requirements
- 8.1.6 Negatively Biased Output
- 8.1.7 Reverse Current Protection
- 8.1.8 Power Dissipation (PD)
- 8.1.1
External Component Selection
- 8.2 Typical Applications
- 8.1
Application Information
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
8.1.2.2 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
The UVLO circuits ensure that the device stays disabled before its input or bias supplies reach the minimum operational voltage range, and ensures that the device properly shuts down when either the input or bias supply collapses.
Figure 8-4 and Table 8-7 explain one of the UVLO circuits being triggered to various input voltage events, assuming VEN ≥ VIH(EN).
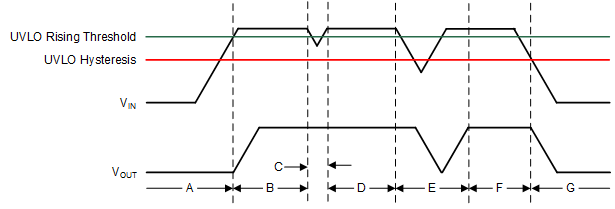 Figure 8-4 Typical UVLO Operation
Figure 8-4 Typical UVLO Operation| REGION | EVENT | VOUT STATUS | COMMENT |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Turnon, VIN ≥ VUVLO_1,2(IN) and VBIAS ≥ VUVLO(BIAS) | Off | Start-up |
| B | Regulation | On | Regulates to target VOUT |
| C | Brownout, VIN ≥ VUVLO_1,2(IN) – VHYS_1,2(IN) or VBIAS ≥ VUVLO(BIAS) – VHYS(BIAS) | On | The output can fall out of regulation but the device is still enabled. |
| D | Regulation | On | Regulates to target VOUT |
| E | Brownout, VIN < VUVLO_1,2(IN) – VHYS_1,2(IN) or VBIAS ≥ VUVLO(BIAS) – VHYS(BIAS) | Off | The device is disabled and the output falls because of the load and active discharge circuit. The device is reenabled when the UVLO fault is removed when either the IN or BIAS UVLO rising threshold is reached by the input or bias voltage and a normal start-up then follows. |
| F | Regulation | On | Regulates to target VOUT |
| G | Turnoff, VIN < VUVLO_1,2(IN) – VHYS_1,2(IN) or VBIAS < VUVLO(BIAS) – VHYS(BIAS) | Off | The output falls because of the load and active discharge circuit. |
Similar to many other LDOs with this feature, the UVLO circuits take a few microseconds to fully assert. During this time, a downward line transient below approximately 0.8 V causes the UVLO to assert for a short time; however, the UVLO circuits do not have enough stored energy to fully discharge the internal circuits inside of the device. When the UVLO circuits are not given enough time to fully discharge the internal nodes, the outputs are not fully disabled.
The effect of the downward line transient can be mitigated by using a larger input capacitor to increase the fall time of the input supply when operating near the minimum VIN.