-
具有高 CMTI 的 AMC1306x 小型、高精度、增强型隔离式 Δ-Σ 调制器 ZHCSG26C March 2017 – Janaury 2020 AMC1306E05 , AMC1306E25 , AMC1306M05 , AMC1306M25
PRODUCTION DATA.
-
具有高 CMTI 的 AMC1306x 小型、高精度、增强型隔离式 Δ-Σ 调制器
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Power Ratings
- 7.6 Insulation Specifications
- 7.7 Safety-Related Certifications
- 7.8 Safety Limiting Values
- 7.9 Electrical Characteristics: AMC1306x05
- 7.10 Electrical Characteristics: AMC1306x25
- 7.11 Switching Characteristics
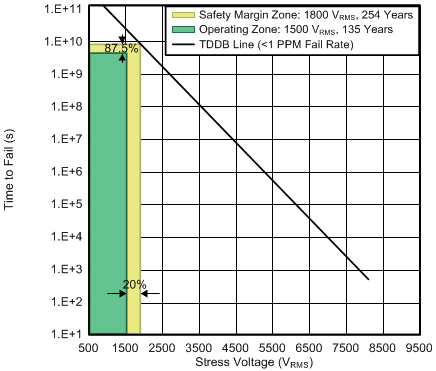
- 7.12 Insulation Characteristics Curves
- 7.13 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
- 重要声明
2 应用
- 基于分流电阻器的电流感应和隔离式电压测量,包括:
- 工业电机驱动
- 光电逆变器
- 不间断电源
3 说明
AMC1306 是一款高精度 Δ-Σ 调制器,通过抗电磁干扰性能极强的电容式双隔离层将输出与输入电路隔离开。该隔离层经过认证,可以按照 DIN VDE V 0884-11 和 UL1577 标准提供高达 7000VPEAK 的增强型隔离。与隔离式电源结合使用时,该隔离式调制器可将以不同共模电压等级运行的系统的各器件隔开,并防止较低电压器件损坏。
AMC1306 的输入针对直接连接分流电阻器或其他低电压等级信号源进行了优化。器件具有独特的 ±50mV 低输入电压范围,可通过分流器显著降低功率耗散,同时具有出色的交流和直流性能。AMC1306 的输出位流采用曼彻斯特编码 (AMC1306Ex) 或未编码 (AMC1306Mx),具体情况因导数而异。通过使用集成式数字滤波器(如 TMS320F2807x 或 TMS320F2837x 微控制器系列中的滤波器)来抽取位流,该器件可在 78kSPS 数据速率下实现 85dB 动态范围的 16 位分辨率。
曼彻斯特编码的 AMC1306Ex 版本的位流输出支持单线数据和时钟传输,无需考虑接收设备的设置和保持时间要求。
器件信息(1)
| 器件型号 | 封装 | 封装尺寸(标称值) |
|---|---|---|
| AMC1306x | SOIC (8) | 5.85mm × 7.50mm |
- 如需了解所有可用封装,请参阅数据表末尾的可订购米6体育平台手机版_好二三四附录。
Device Images
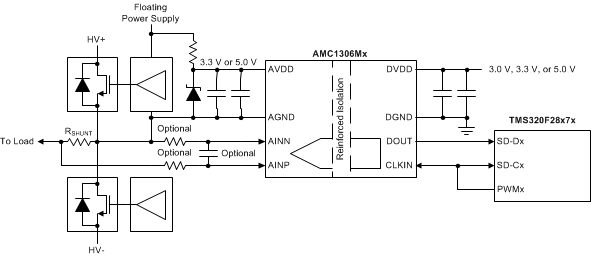
简化原理图
4 修订历史记录
Changes from B Revision (June 2018) to C Revision
- Changed 更改了安全相关认证 项目符号(位于特性 部分):将 VDE 认证 版本从 DIN V VDE V 0884-10 (VDE V 0884-11) 更改为 DIN VDE V 0884-11,并将 IEC 60950-1 和 IEC 60065 更改为 IEC 62368-1Go
- Changed 将 DIN V VDE V 更改为 DIN VDE V(位于说明 部分)Go
- Changed CLR and CPG values from ≥ 9 mm to ≥ 8.5 mm in Insulation Specifications tableGo
- Changed Insulation Specifications table header row from DIN V VDE V 0884-11 (VDE V 0884-11): 2017-01 to DIN VDE V 0884-11: 2017-01Go
- Changed VDE certification details in Safety-Related Certifications tableGo
- Changed Safety Limiting Values table format as per current standardGo
- Changed free air to ambient in condition statement of Switching Characteristics tableGo
- Changed 6.05 dB to 6.02 dB in Equation 3Go
- Changed input common-mode voltage from 2 V to 1.9 V for consistency with Input Bias Current vs Common-Mode Input Voltage figure in What To Do and What Not To Do sectionGo
- Changed VINx to AINx in Layout Guidelines sectionGo
- Changed Recommended Layout of the AMC1306x figure to include connection to the shunt resistor and input filter componentsGo
Changes from A Revision (July 2017) to B Revision
- Changed Reinforced Isolation Capacitor Lifetime Projection figure Go
Changes from * Revision (March 2017) to A Revision
- AMC1306E05 和 AMC1306M05 已投入生产Go
- Added 向第一个直流性能 子项目符号中添加了 ±50µV,以反映 AMC1306x05 器件的情况Go
- Changed 将第一个安全相关认证 子项目符号中的标准偏差从 0884-10 更改为 0884-11Go
- Changed 将 VPEAK 从 8000 更改为 7000,将标准偏差从 0884-10 变更为 0884-11(均位于说明 部分的第一段)Go
- Deleted Status column from Device Comparison TableGo
- Changed standard deviation from 0884-10 to 0884-11 in DIN V VDE V 0884-11 section of Insulation Specifications tableGo
- Changed standard deviation from 0884-10 to 0884-11 in Safety-Related Certifications tableGo
- Changed prevent to minimize in condition statement of Safety Limiting Values tableGo
- Added Electrical Characteristics: AMC1306x05 table Go
- Changed test conditions of Analog Inputs test conditions from (AINP – AINN) / 2 to AGND to (AINP + AINN) / 2 to AGND to include all possible conditionsGo
- Changed IIB test condition from Inputs shorted to AGND to AINP = AINN = AGND, IIB = IIBP + IIBNGo
- Added AINP = AINN = AGND to EO parameter test conditions Go
- Changed minus sign to plus or minus sign in typical specification of EG parameter Go
- Changed 10% to 90% to 90% to 10% in test conditions of tf parameter Go
- Added AMC1306x05 devices to Typical Characteristics section Go
6 Pin Configuration and Functions
Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NO. | NAME | ||
| 1 | AVDD | — | Analog (high-side) power supply, 3.0 V to 5.5 V.
See the Power Supply Recommendations section for decoupling recommendations. |
| 2 | AINP | I | Noninverting analog input |
| 3 | AINN | I | Inverting analog input |
| 4 | AGND | — | Analog (high-side) ground reference |
| 5 | DGND | — | Digital (controller-side) ground reference |
| 6 | DOUT | O | Modulator data output. This pin is a Manchester coded output for AMC1306Ex derivates. |
| 7 | CLKIN | I | Modulator clock input: 5 MHz to 21 MHz (5-V operation) with internal pulldown resistor (typical value: 1.5 MΩ) |
| 8 | DVDD | — | Digital (controller-side) power supply, 2.7 V to 5.5 V.
See the Power Supply Recommendations section for decoupling recommendations. |
7 Specifications
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings(1)
| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage | AVDD to AGND or DVDD to DGND | –0.3 | 6.5 | V |
| Analog input voltage at AINP, AINN | AGND – 6 | AVDD + 0.5 | V | |
| Digital input or output voltage at CLKIN or DOUT | DGND – 0.5 | DVDD + 0.5 | V | |
| Input current to any pin except supply pins | –10 | 10 | mA | |
| Junction temperature, TJ | 150 | °C | ||
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –65 | 150 | °C | |
7.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±2000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±1000 | |||
7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating ambient temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVDD | Analog (high-side) supply voltage (AVDD to AGND) | 3.0 | 5.0 | 5.5 | V |
| DVDD | Digital (controller-side) supply voltage (DVDD to DGND) | 2.7 | 3.3 | 5.5 | V |
| TA | Operating ambient temperature | –40 | 125 | °C | |
7.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC (1) | AMC1306x | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DWV (SOIC) | |||
| 8 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 112.2 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 47.6 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 60.0 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 23.1 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 60.0 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | n/a | °C/W |
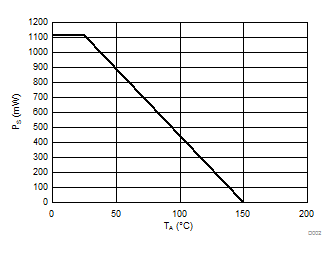
7.5 Power Ratings
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PD | Maximum power dissipation
(both sides) |
AMC1306Ex, AVDD = DVDD = 5.5 V | 91.85 | mW | ||
| AMC1306Mx, AVDD = DVDD = 5.5 V | 86.90 | |||||
| PD1 | Maximum power dissipation
(high-side supply) |
AVDD = 5.5 V | 53.90 | mW | ||
| PD2 | Maximum power dissipation
(low-side supply) |
AMC1306Ex, DVDD = 5.5 V | 37.95 | mW | ||
| AMC1306Mx, DVDD = 5.5 V | 33.00 | |||||
7.6 Insulation Specifications
over operating ambient temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | VALUE | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GENERAL | ||||
| CLR | External clearance(1) | Shortest pin-to-pin distance through air | ≥ 8.5 | mm |
| CPG | External creepage(1) | Shortest pin-to-pin distance across the package surface | ≥ 8.5 | mm |
| DTI | Distance through insulation | Minimum internal gap (internal clearance) of the double insulation (2 × 0.0105 mm) | ≥ 0.021 | mm |
| CTI | Comparative tracking index | DIN EN 60112 (VDE 0303-11); IEC 60112 | ≥ 600 | V |
| Material group | According to IEC 60664-1 | I | ||
| Overvoltage category per IEC 60664-1 | Rated mains voltage ≤ 300 VRMS | I-IV | ||
| Rated mains voltage ≤ 600 VRMS | I-IV | |||
| Rated mains voltage ≤ 1000 VRMS | I-III | |||
| DIN VDE V 0884-11: 2017-01(2) | ||||
| VIORM | Maximum repetitive peak isolation voltage | At ac voltage (bipolar) | 2121 | VPK |
| VIOWM | Maximum-rated isolation working voltage | At ac voltage (sine wave) | 1500 | VRMS |
| At dc voltage | 2121 | VDC | ||
| VIOTM | Maximum transient isolation voltage | VTEST = VIOTM, t = 60 s (qualification test) | 7000 | VPK |
| VTEST = 1.2 × VIOTM, t = 1 s (100% production test) | 8400 | |||
| VIOSM | Maximum surge isolation voltage(3) | Test method per IEC 60065, 1.2/50-μs waveform,
VTEST = 1.6 × VIOSM = 12800 VPK (qualification) |
8000 | VPK |
| qpd | Apparent charge(4) | Method a, after input/output safety test subgroup 2/3,
Vini = VIOTM, tini = 60 s, Vpd(m) = 1.2 × VIORM = 2545 VPK, tm = 10 s |
≤ 5 | pC |
| Method a, after environmental tests subgroup 1,
Vini = VIOTM, tini = 60 s, Vpd(m) = 1.6 × VIORM = 3394 VPK, tm = 10 s |
≤ 5 | |||
| Method b1, at routine test (100% production) and preconditioning (type test), Vini = VIOTM, tini = 1 s,
Vpd(m) = 1.875 × VIORM = 3977 VPK, tm = 1 s |
≤ 5 | |||
| CIO | Barrier capacitance, input to output(5) | VIO = 0.5 VPP at 1 MHz | ~1 | pF |
| RIO | Insulation resistance, input to output(5) | VIO = 500 V at TA = 25°C | > 1012 | Ω |
| VIO = 500 V at 100°C ≤ TA ≤ 125°C | > 1011 | |||
| VIO = 500 V at TS = 150°C | > 109 | |||
| Pollution degree | 2 | |||
| Climatic category | 40/125/21 | |||
| UL1577 | ||||
| VISO | Withstand isolation voltage | VTEST = VISO = 5000 VRMS or 7000 VDC, t = 60 s (qualification), VTEST = 1.2 × VISO = 6000 VRMS, t = 1 s (100% production test) | 5000 | VRMS |
7.7 Safety-Related Certifications
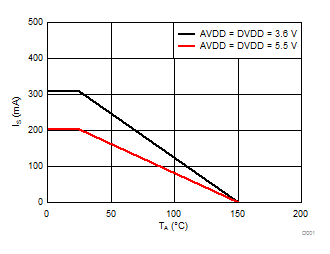
7.8 Safety Limiting Values
Safety limiting intends to minimize potential damage to the isolation barrier upon failure of input or output circuitry.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IS | Safety input, output, or supply current | RθJA = 112.2°C/W, AVDD = DVDD = 5.5 V,
TJ = 150°C, TA = 25°C |
202.5 | mA | ||
| RθJA = 112.2°C/W, AVDD = DVDD = 3.6 V,
TJ = 150°C, TA = 25°C |
309.4 | |||||
| PS | Safety input, output, or total power | RθJA = 112.2°C/W, TJ = 150°C, TA = 25°C | 1114(1) | mW | ||
| TS | Maximum safety temperature | 150 | °C | |||
The junction-to-air thermal resistance, RθJA, in the Thermal Information table is that of a device installed on a high-K test board for leaded surface-mount packages. Use these equations to calculate the value for each parameter:
TJ = TA + RθJA × P, where P is the power dissipated in the device.
TJ(max) = TS = TA + RθJA × PS, where TJ(max) is the maximum junction temperature.
PS = IS × AVDDmax + IS × AVDDmax, where AVDDmax is the maximum high-side supply voltage and DVDDmax is the maximum controller-side supply voltage.
7.9 Electrical Characteristics: AMC1306x05
minimum and maximum specifications apply from TA = –40°C to +125°C, AVDD = 3.0 V to 5.5 V, DVDD = 2.7 V to 5.5 V, AINP = –50 mV to 50 mV, AINN = AGND, and sinc3 filter with OSR = 256 (unless otherwise noted); typical specifications are at TA = 25°C, CLKIN = 20 MHz, AVDD = 5 V, and DVDD = 3.3 V| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANALOG INPUTS | ||||||
| VClipping | Differential input voltage before clipping output | VIN = AINP – AINN | ±64 | mV | ||
| FSR | Specified linear differential full-scale | VIN = AINP – AINN | –50 | 50 | mV | |
| Absolute common-mode input voltage(1) | (AINP + AINN) / 2 to AGND | –2 | AVDD | V | ||
| VCM | Operating common-mode input voltage | (AINP + AINN) / 2 to AGND | –0.032 | AVDD – 2.1 | V | |
| VCMov | Common-mode overvoltage detection level(2) | (AINP + AINN) / 2 to AGND | AVDD - 2 | V | ||
| CIN | Single-ended input capacitance | AINN = AGND | 4 | pF | ||
| CIND | Differential input capacitance | 2 | pF | |||
| IIB | Input bias current | AINP = AINN = AGND, IIB = IIBP + IIBN | –97 | –72 | –57 | μA |
| RIN | Single-ended input resistance | AINN = AGND | 4.75 | kΩ | ||
| RIND | Differential input resistance | 4.9 | kΩ | |||
| IIO | Input offset current | ±10 | nA | |||
| CMTI | Common-mode transient immunity | 50 | 100 | kV/μs | ||
| CMRR | Common-mode rejection ratio | AINP = AINN, fIN = 0 Hz,
VCM min ≤ VIN ≤ VCM max |
–99 | dB | ||
| AINP = AINN, fIN from 0.1 Hz to 50 kHz,
VCM min ≤ VIN ≤ VCM max |
–98 | |||||
| BW | Input bandwidth(3) | 800 | kHz | |||
| DC ACCURACY | ||||||
| DNL | Differential nonlinearity | Resolution: 16 bits | –0.99 | 0.99 | LSB | |
| INL | Integral nonlinearity(4) | Resolution: 16 bits, 4.5 V ≤ AVDD ≤ 5.5 V | –4 | ±1 | 4 | LSB |
| Resolution: 16 bits, 3.0 V ≤ AVDD ≤ 3.6 V | –5 | ±1.5 | 5 | |||
| EO | Offset error | Initial, at 25°C, AINP = AINN = AGND | –50 | ±2.5 | 50 | µV |
| TCEO | Offset error thermal drift(5) | –1 | ±0.25 | 1 | μV/°C | |
| EG | Gain error | Initial, at 25°C | –0.2% | ±0.005% | 0.2% | |
| TCEG | Gain error thermal drift(6) | –40 | ±20 | 40 | ppm/°C | |
| PSRR | Power-supply rejection ratio | AINP = AINN = AGND,
3.0 V ≤ AVDD ≤ 5.5 V, at dc |
–108 | dB | ||
| AINP = AINN = AGND,
3.0 V ≤ AVDD ≤ 5.5 V, 10 kHz, 100-mV ripple |
–107 | |||||
| AC ACCURACY | ||||||
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio | fIN = 1 kHz | 78 | 82.5 | dB | |
| SINAD | Signal-to-noise + distortion | fIN = 1 kHz | 77.5 | 82.3 | dB | |
| THD | Total harmonic distortion | 4.5 V ≤ AVDD ≤ 5.5 V,
5 MHz ≤ fCLKIN ≤ 21 MHz, fIN = 1 kHz |
–98 | –84 | dB | |
| 3.0 V ≤ AVDD ≤ 3.6 V,
5 MHz ≤ fCLKIN ≤ 20 MHz, fIN = 1 kHz |
–93 | –83 | ||||
| SFDR | Spurious-free dynamic range | fIN = 1 kHz | 83 | 100 | dB | |
| DIGITAL INPUTS/OUTPUTS | ||||||
| CMOS Logic With Schmitt-Trigger | ||||||
| IIN | Input current | DGND ≤ VIN ≤ DVDD | 0 | 7 | µA | |
| CIN | Input capacitance | 4 | pF | |||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | 0.7 × DVDD | DVDD + 0.3 | V | ||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | –0.3 | 0.3 × DVDD | V | ||
| CLOAD | Output load capacitance | 30 | pF | |||
| VOH | High-level output voltage | IOH = –20 µA | DVDD – 0.1 | V | ||
| IOH = –4 mA | DVDD – 0.4 | |||||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage | IOL = 20 µA | 0.1 | V | ||
| IOL = 4 mA | 0.4 | |||||
| POWER SUPPLY | ||||||
| AVDD | High-side supply voltage | 3.0 | 5.0 | 5.5 | V | |
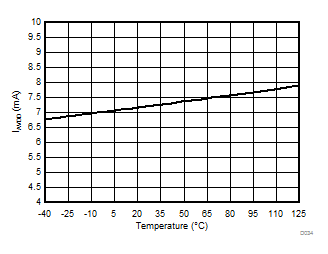
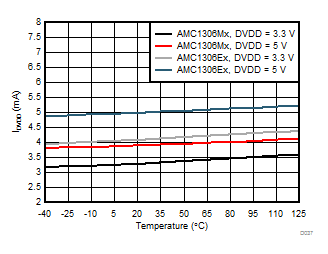
| IAVDD | High-side supply current | 3.0 V ≤ AVDD ≤ 3.6 V | 6.3 | 8.5 | mA | |
| 4.5 V ≤ AVDD ≤ 5.5 V | 7.2 | 9.8 | ||||
| DVDD | Controller-side supply voltage | 2.7 | 3.3 | 5.5 | V | |
| IDVDD | Controller-side supply current | AMC1306Ex, 2.7 V ≤ DVDD ≤ 3.6 V,
CLOAD = 15 pF |
4.1 | 5.5 | mA | |
| AMC1306Mx, 2.7 V ≤ DVDD ≤ 3.6 V,
CLOAD = 15 pF |
3.3 | 4.8 | ||||
| AMC1306Ex, 4.5 V ≤ DVDD ≤ 5.5 V,
CLOAD = 15 pF |
5.0 | 6.9 | ||||
| AMC1306Mx, 4.5 V ≤ DVDD ≤ 5.5 V,
CLOAD = 15 pF |
3.9 | 6.0 | ||||
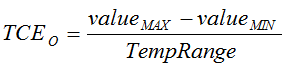
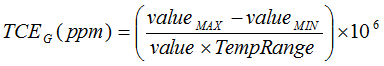
7.10 Electrical Characteristics: AMC1306x25
minimum and maximum specifications apply from TA = –40°C to +125°C, AVDD = 3.0 V to 5.5 V, DVDD = 2.7 V to 5.5 V, AINP = –250 mV to 250 mV, AINN = AGND, and sinc3 filter with OSR = 256 (unless otherwise noted); typical specifications are at TA = 25°C, CLKIN = 20 MHz, AVDD = 5 V, and DVDD = 3.3 V| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANALOG INPUTS | ||||||
| VClipping | Differential input voltage before clipping output | AINP – AINN | ±320 | mV | ||
| FSR | Specified linear differential full-scale | AINP – AINN | –250 | 250 | mV | |
| Absolute common-mode input voltage(1) | (AINP + AINN) / 2 to AGND | –2 | AVDD | V | ||
| VCM | Operating common-mode input voltage | (AINP + AINN) / 2 to AGND | –0.16 | AVDD – 2.1 | V | |
| VCMov | Common-mode overvoltage detection level(2) | (AINP + AINN) / 2 to AGND | AVDD – 2 | V | ||
| CIN | Single-ended input capacitance | AINN = AGND | 2 | pF | ||
| CIND | Differential input capacitance | 1 | pF | |||
| IIB | Input bias current | AINP = AINN = AGND, IIB = IIBP + IIBN | –82 | –60 | –48 | µA |
| RIN | Single-ended input resistance | AINN = AGND | 19 | kΩ | ||
| RIND | Differential input resistance | 22 | kΩ | |||
| IIO | Input offset current | ±5 | nA | |||
| CMTI | Common-mode transient immunity | 50 | 100 | kV/µs | ||
| CMRR | Common-mode rejection ratio | AINP = AINN, fIN = 0 Hz,
VCM min ≤ VIN ≤ VCM max |
–95 | dB | ||
| AINP = AINN, fIN from 0.1 Hz to 50 kHz,
VCM min ≤ VIN ≤ VCM max |
–95 | |||||
| BW | Input bandwidth(3) | 900 | kHz | |||
| DC ACCURACY | ||||||
| DNL | Differential nonlinearity | Resolution: 16 bits | –0.99 | 0.99 | LSB | |
| INL | Integral nonlinearity(4) | Resolution: 16 bits | –4 | ±1 | 4 | LSB |
| EO | Offset error | Initial, at 25°C, AINP = AINN = AGND | –100 | ±4.5 | 100 | µV |
| TCEO | Offset error thermal drift(5) | –1 | ±0.15 | 1 | µV/°C | |
| EG | Gain error | Initial, at 25°C | –0.2% | ±0.005% | 0.2% | |
| TCEG | Gain error thermal drift(6) | –40 | ±20 | 40 | ppm/°C | |
| PSRR | Power-supply rejection ratio | AINP = AINN = AGND,
3.0 V ≤ AVDD ≤ 5.5 V, at dc |
–103 | dB | ||
| AINP = AINN = AGND,
3.0 V ≤ AVDD ≤ 5.5 V, 10 kHz, 100-mV ripple |
–92 | |||||
| AC ACCURACY | ||||||
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio | fIN = 1 kHz | 82 | 86 | dB | |
| SINAD | Signal-to-noise + distortion | fIN = 1 kHz | 81.9 | 85.7 | dB | |
| THD | Total harmonic distortion | 4.5 V ≤ AVDD ≤ 5.5 V,
5 MHz ≤ fCLKIN ≤ 21 MHz, fIN = 1 kHz |
–98 | –86 | dB | |
| 3.0 V ≤ AVDD ≤ 3.6 V,
5 MHz ≤ fCLKIN ≤ 20 MHz, fIN = 1 kHz |
–93 | –85 | ||||
| SFDR | Spurious-free dynamic range | fIN = 1 kHz | 83 | 100 | dB | |
| DIGITAL INPUTS/OUTPUTS | ||||||
| CMOS Logic with Schmitt-trigger | ||||||
| IIN | Input current | DGND ≤ VIN ≤ DVDD | 0 | 7 | μA | |
| CIN | Input capacitance | 4 | pF | |||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | 0.7 × DVDD | DVDD + 0.3 | V | ||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | –0.3 | 0.3 × DVDD | V | ||
| CLOAD | Output load capacitance | fCLKIN = 20 MHz | 30 | pF | ||
| VOH | High-level output voltage | IOH = –20 µA | DVDD – 0.1 | V | ||
| IOH = –4 mA | DVDD – 0.4 | |||||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage | IOL = 20 µA | 0.1 | V | ||
| IOL = 4 mA | 0.4 | |||||
| POWER SUPPLY | ||||||
| AVDD | High-side supply voltage | 3.0 | 5.0 | 5.5 | V | |
| IAVDD | High-side supply current | 3.0 V ≤ AVDD ≤ 3.6 V | 6.3 | 8.5 | mA | |
| 4.5 V ≤ AVDD ≤ 5.5 V | 7.2 | 9.8 | ||||
| DVDD | Controller-side supply voltage | 2.7 | 3.3 | 5.5 | V | |
| IDVDD | Controller-side supply current | AMC1306Ex, 2.7 V ≤ DVDD ≤ 3.6 V,
CLOAD = 15 pF |
4.1 | 5.5 | mA | |
| AMC1306Mx, 2.7 V ≤ DVDD ≤ 3.6 V,
CLOAD = 15 pF |
3.3 | 4.8 | ||||
| AMC1306Ex, 4.5 V ≤ DVDD ≤ 5.5 V,
CLOAD = 15 pF |
5.0 | 6.9 | ||||
| AMC1306Mx, 4.5 V ≤ DVDD ≤ 5.5 V,
CLOAD = 15 pF |
3.9 | 6.0 | ||||
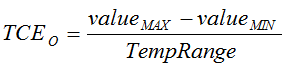 .
. 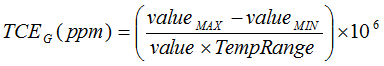 .
.7.11 Switching Characteristics
over operating ambient temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
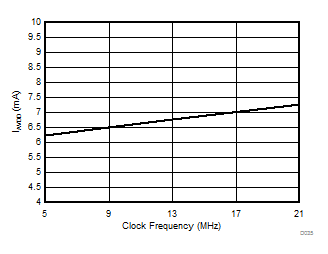
| fCLKIN | CLKIN clock frequency | 4.5 V ≤ AVDD ≤ 5.5 V | 5 | 21 | MHz | |
| 3.0 V ≤ AVDD ≤ 5.5 V | 5 | 20 | ||||
| tCLKIN | CLKIN clock period | 4.5 V ≤ AVDD ≤ 5.5 V | 47.6 | 200 | ns | |
| 3.0 V ≤ AVDD ≤ 5.5 V | 50 | 200 | ||||
| tHIGH | CLKIN clock high time | 20 | 25 | 120 | ns | |
| tLOW | CLKIN clock low time | 20 | 25 | 120 | ns | |
| tH | DOUT hold time after rising edge
of CLKIN |
AMC1306Mx(1),
CLOAD = 15 pF |
3.5 | ns | ||
| tD | Rising edge of CLKIN to DOUT valid delay | AMC1306Mx(1), CLOAD = 15 pF | 15 | ns | ||
| tr | DOUT rise time | 10% to 90%, 2.7 V ≤ DVDD ≤ 3.6 V,
CLOAD = 15 pF |
0.8 | 3.5 | ns | |
| 10% to 90%, 4.5 V ≤ DVDD ≤ 5.5 V,
CLOAD = 15 pF |
1.8 | 3.9 | ||||
| tf | DOUT fall time | 90% to 10%, 2.7 V ≤ DVDD ≤ 3.6 V,
CLOAD = 15 pF |
0.8 | 3.5 | ns | |
| 90% to 10%, 4.5 V ≤ DVDD ≤ 5.5 V,
CLOAD = 15 pF |
1.8 | 3.9 | ||||
| tISTART | Interface startup time | DVDD at 2.7 V (min) to DOUT valid with AVDD ≥ 3.0 V | 32 | 32 | CLKIN cycles | |
| tASTART | Analog startup time | AVDD step to 3.0 V with DVDD ≥ 2.7 V, 0.1% settling | 0.5 | ms | ||
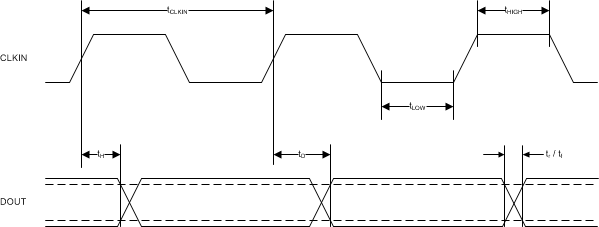 Figure 1. Digital Interface Timing
Figure 1. Digital Interface Timing 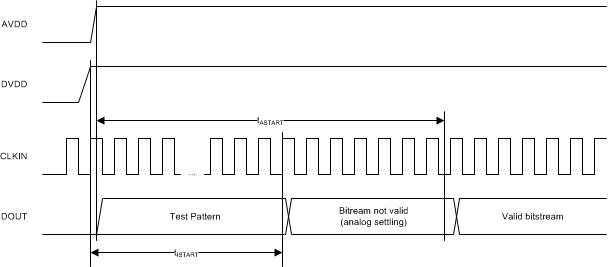 Figure 2. Device Startup Timing
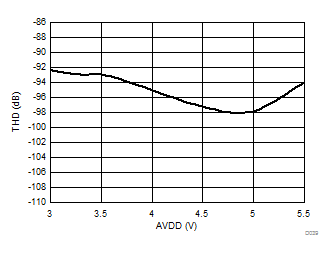
Figure 2. Device Startup Timing 7.12 Insulation Characteristics Curves
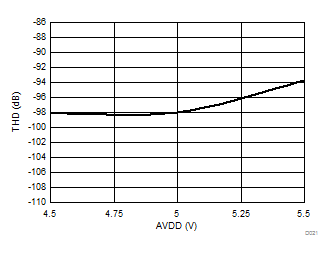
Power per VDE
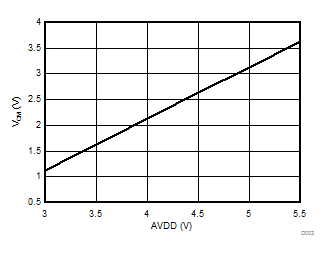
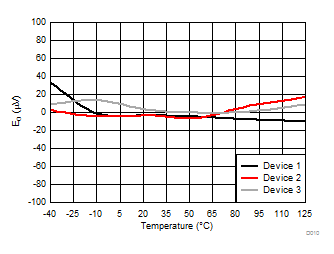
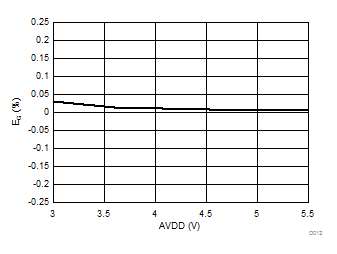
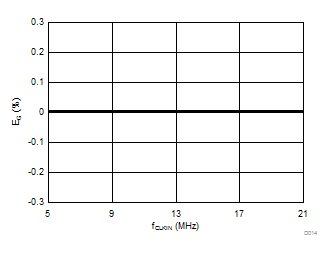
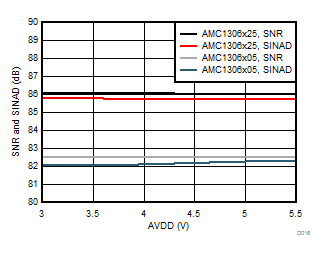
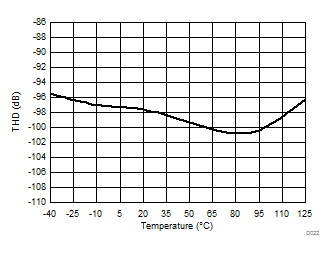
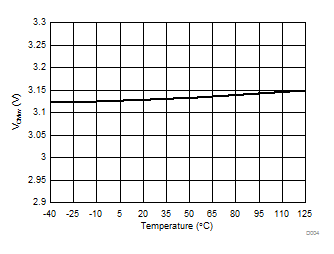
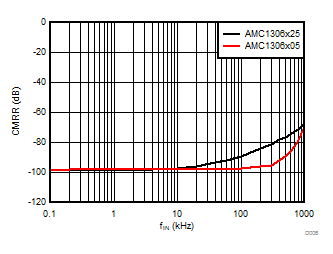
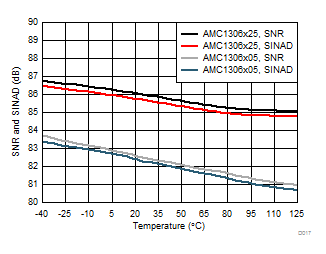
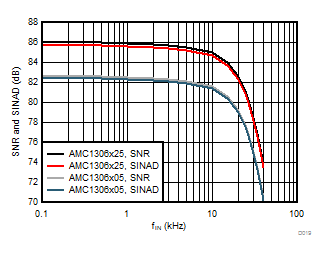
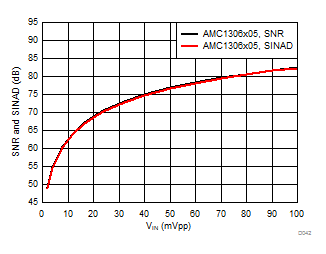
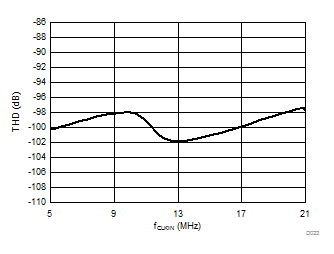
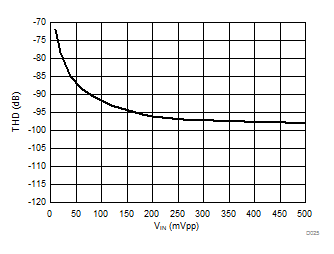
7.13 Typical Characteristics
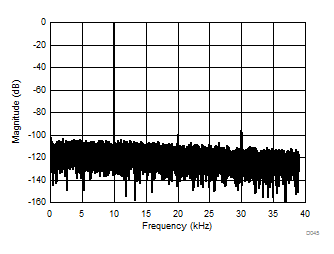
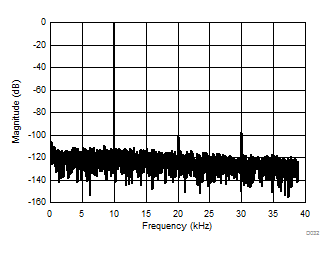
at AVDD = 5 V, DVDD = 3.3 V, AINP = –50 mV to 50 mV (AMC1306x05) or –250 mV to 250 mV (AMC1306x25), AINN = AGND, fCLKIN = 20 MHz, and sinc3 filter with OSR = 256 (unless otherwise noted)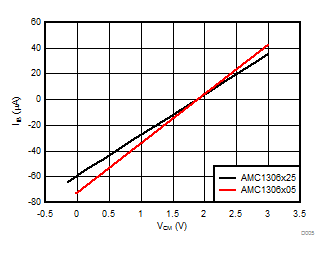
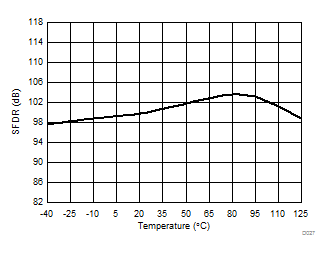
Common-Mode Input Voltage

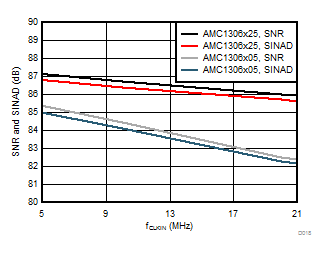
| fCLKIN = 21 MHz |
High-Side Supply Voltage (5 V, nom)
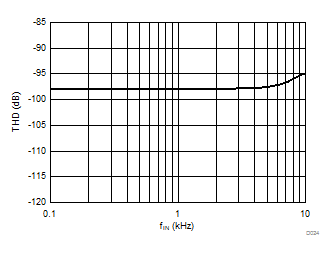
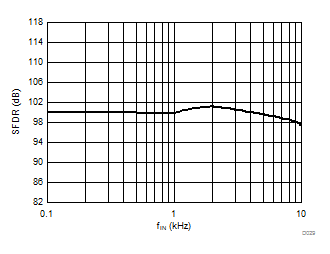
Input Signal Frequency
| AMC1306x05 |
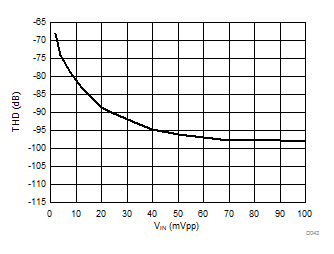
Input Signal Amplitude
Input Signal Frequency
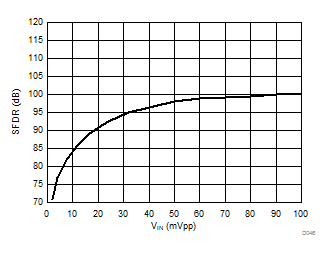
| AMC1306x05 |
Input Signal Amplitude
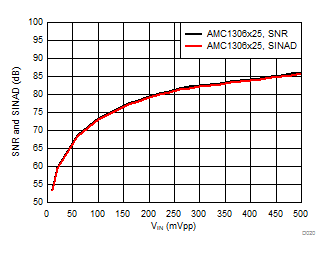
| AMC1306x05, 4096-point FFT, VIN = 100 mVPP |
| AMC1306x25, 4096-point FFT, VIN = 500 mVPP |
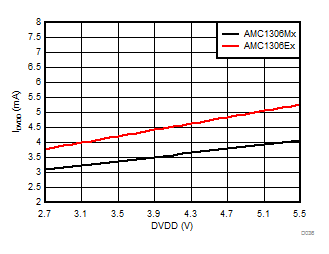
Controller-Side Supply Voltage
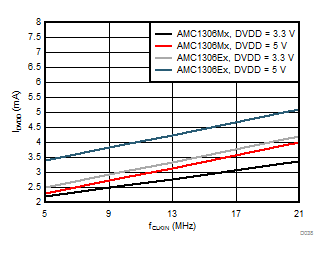
Clock Frequency
Input Signal Frequency
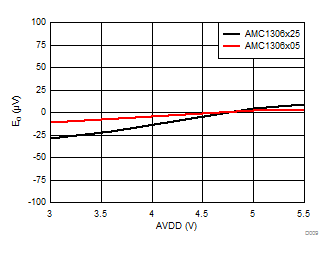
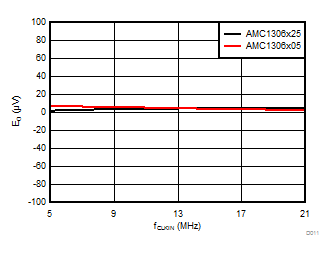
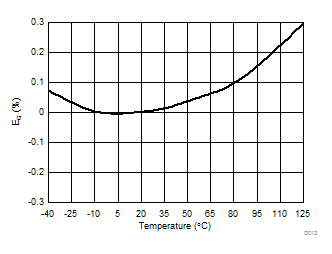
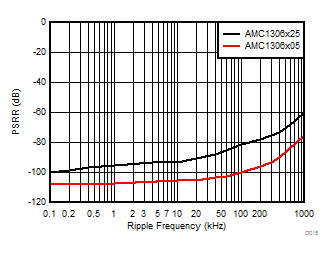
Ripple Frequency
| fCLKIN = 20 MHz |
High-Side Supply Voltage (3.3 V, nom)
| AMC1306x25 |
Input Signal Amplitude
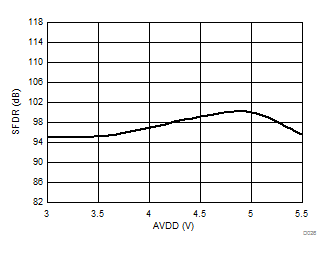
High-Side Supply Voltage
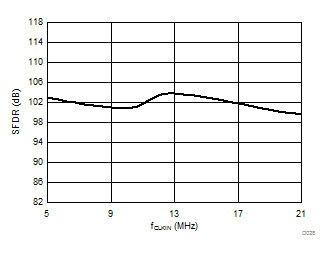
Clock Frequency
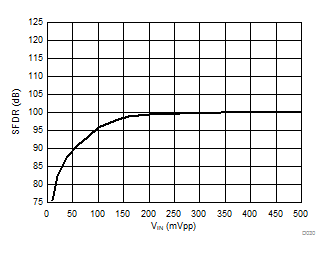
| AMC1306x25 |
Input Signal Amplitude
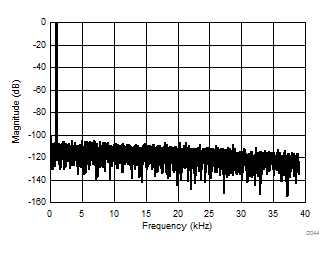
| AMC1306x05, 4096-point FFT, VIN = 100 mVPP |
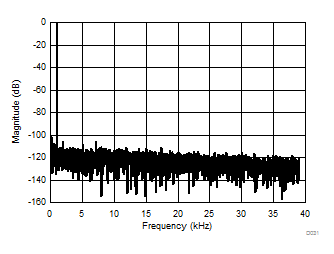
| AMC1306x25, 4096-point FFT, VIN = 500 mVPP |
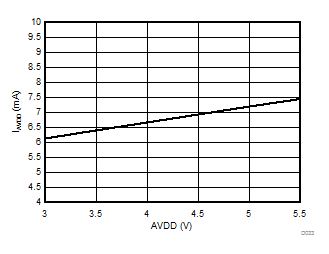
High-Side Supply Voltage
8 Detailed Description
8.1 Overview
The differential analog input (comprised of input signals AINP and AINN) of the AMC1306 is a fully-differential amplifier feeding the switched-capacitor input of a second-order, delta-sigma (ΔΣ) modulator stage that digitizes the input signal into a 1-bit output stream. The isolated data output DOUT of the converter provides a stream of digital ones and zeros that is synchronous to the externally-provided clock source at the CLKIN pin with a frequency in the range of 5 MHz to 21 MHz. The time average of this serial bitstream output is proportional to the analog input voltage.
The Functional Block Diagram section shows a detailed block diagram of the AMC1306. The analog input range is tailored to directly accommodate a voltage drop across a shunt resistor used for current sensing. The silicon-dioxide (SiO2) based capacitive isolation barrier supports a high level of magnetic field immunity as described in the ISO72x Digital Isolator Magnetic-Field Immunity application report, available for download at www.ti.com. The external clock input simplifies the synchronization of multiple current-sensing channels on the system level. The extended frequency range of up to 21 MHz supports higher performance levels compared to the other solutions available on the market.
8.2 Functional Block Diagram
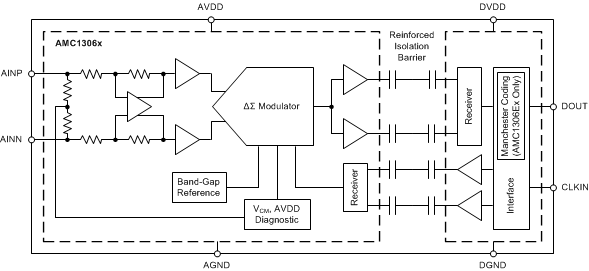
8.3 Feature Description
8.3.1 Analog Input
The AMC1306 incorporates front-end circuitry that contains a differential amplifier and a sampling stage, followed by a ΔΣ modulator. The gain of the differential amplifier is set by internal precision resistors to a factor of 4 for devices with a specified input voltage range of ±250 mV (this value is for the AMC1306x25), or to a factor of 20 in devices with a ±50-mV input voltage range (for the AMC1306x05), resulting in a differential input impedance of 4.9 kΩ (for the AMC1306x05) or 22 kΩ (for the AMC1306x25). For reduced offset and offset drift, the differential amplifier is chopper-stabilized with the switching frequency set at fCLKIN / 32. The switching frequency generates a spur as shown in Figure 47.
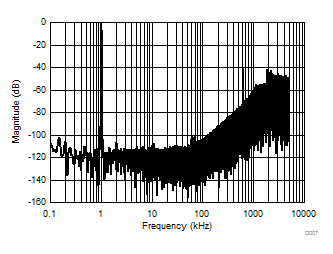
| sinc3 filter, OSR = 2, fCLKIN = 20 MHz, fIN = 1 kHz |
Consider the input impedance of the AMC1306 in designs with high-impedance signal sources that can cause degradation of gain and offset specifications. The importance of this effect, however, depends on the desired system performance. Additionally, the input bias current caused by the internal common-mode voltage at the output of the differential amplifier is dependent on the actual amplitude of the input signal; see the Isolated Voltage Sensing section for more details on reducing these effects.
There are two restrictions on the analog input signals (AINP and AINN). First, if the input voltage exceeds the range AGND – 6 V to AVDD + 0.5 V, the input current must be limited to 10 mA because the device input electrostatic discharge (ESD) diodes turn on. In addition, the linearity and noise performance of the device are ensured only when the differential analog input voltage remains within the specified linear full-scale range (FSR), that is ±250 mV (for the AMC1306x25) or ±50 mV (for the AMC1306x05), and within the specified input common-mode range.
8.3.2 Modulator
The modulator implemented in the AMC1306 is a second-order, switched-capacitor, feed-forward ΔΣ modulator, such as the one conceptualized in Figure 48. The analog input voltage VIN and the output V5 of the 1-bit digital-to-analog converter (DAC) are differentiated, providing an analog voltage V1 at the input of the first integrator stage. The output of the first integrator feeds the input of the second integrator stage, resulting in output voltage V3 that is differentiated with the input signal VIN and the output of the first integrator V2. Depending on the polarity of the resulting voltage V4, the output of the comparator is changed. In this case, the 1-bit DAC responds on the next clock pulse by changing the associated analog output voltage V5, causing the integrators to progress in the opposite direction and forcing the value of the integrator output to track the average value of the input.
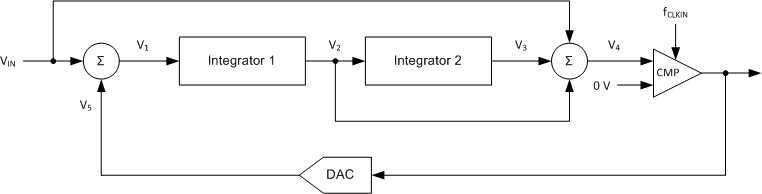 Figure 48. Block Diagram of a Second-Order Modulator
Figure 48. Block Diagram of a Second-Order Modulator The modulator shifts the quantization noise to high frequencies, as shown in Figure 48. Therefore, use a low-pass digital filter at the output of the device to increase the overall performance. This filter is also used to convert from the 1-bit data stream at a high sampling rate into a higher-bit data word at a lower rate (decimation). TI's microcontroller families TMS320F2807x and TMS320F2837x offer a suitable programmable, hardwired filter structure termed a sigma-delta filter module (SDFM) optimized for usage with the AMC1306 family. Also, SD24_B converters on the MSP430F677x microcontrollers offer a path to directly access the integrated sinc-filters for a simple system-level solution for multichannel, isolated current sensing. An additional option is to use a suitable application-specific device, such as the AMC1210 (a four-channel digital sinc-filter). Alternatively, a field-programmable gate array (FPGA) can be used to implement the filter.
8.3.3 Isolation Channel Signal Transmission
The AMC1306 device uses an on-off keying (OOK) modulation scheme to transmit the modulator output bitstream across the capacitive SiO2-based isolation barrier. The transmitter modulates the bitstream at TX IN in Figure 49 with an internally-generated, 480-MHz carrier across the isolation barrier to represent a digital one and sends a no signal to represent the digital zero. The receiver demodulates the signal after advanced signal conditioning and produces the output. The symmetrical design of each isolation channel improves the CMTI performance and reduces the radiated emissions caused by the high-frequency carrier. The block diagram of an isolation channel integrated in the AMC1306 is shown in Figure 49.
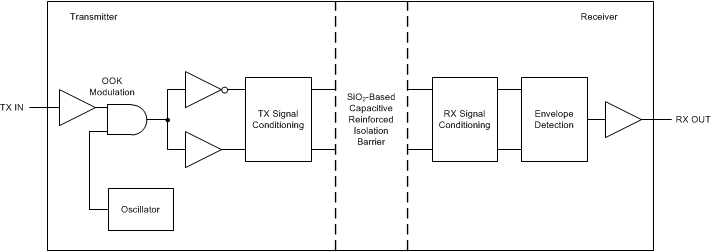 Figure 49. Block Diagram of an Isolation Channel
Figure 49. Block Diagram of an Isolation Channel Figure 50 shows the concept of the on-off keying scheme.
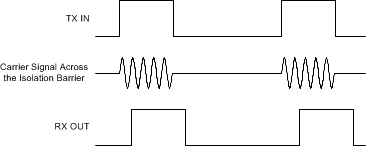 Figure 50. OOK-Based Modulation Scheme
Figure 50. OOK-Based Modulation Scheme 8.3.4 Digital Output
A differential input signal of 0 V ideally produces a stream of ones and zeros that are high 50% of the time. A differential input of 250 mV (for the AMC1306x25) or 50 mV (for the AMC1306x05) produces a stream of ones and zeros that are high 89.06% of the time. With 16 bits of resolution, that percentage ideally corresponds to the code 58368. A differential input of –250 mV (–50 mV for the AMC1306x05) produces a stream of ones and zeros that are high 10.94% of the time and ideally results in code 7168 with 16-bit resolution. These input voltages are also the specified linear ranges of the different AMC1306 versions with performance as specified in this document. If the input voltage value exceeds these ranges, the output of the modulator shows nonlinear behavior when the quantization noise increases. The output of the modulator clips with a stream of only zeros with an input less than or equal to –320 mV (–64 mV for the AMC1306x05) or with a stream of only ones with an input greater than or equal to 320 mV (64 mV for the AMC1306x05). In this case, however, the AMC1306 generates a single 1 (if the input is at negative full-scale) or 0 every 128 clock cycles to indicate proper device function (see the Fail-Safe Output section for more details). The input voltage versus the output modulator signal is shown in Figure 51.
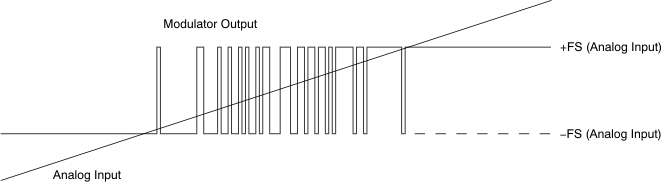 Figure 51. Analog Input versus the AMC1306 Modulator Output
Figure 51. Analog Input versus the AMC1306 Modulator Output The density of ones in the output bitstream for any input voltage value (with the exception of a full-scale input signal, as described in the Output Behavior in Case of a Full-Scale Input section) can be calculated using Equation 1:
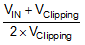
The AMC1306 system clock is provided externally at the CLKIN pin. For more details, see the Switching Characteristics table and the Manchester Coding Feature section.
8.3.5 Manchester Coding Feature
The AMC1306Ex offers the IEEE 802.3-compliant Manchester coding feature that generates at least one transition per bit to support clock signal recovery from the bitstream. A Manchester coded bitstream is free of dc components. The Manchester coding combines the clock and data information using exclusive or (XOR) logical operation and results in a bitstream as shown in Figure 52. The duty cycle of the Manchester encoded bitstream depends on the duty cycle of the input clock CLKIN.
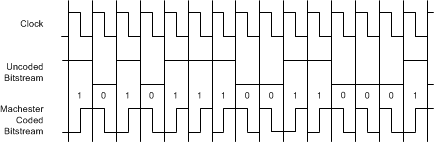 Figure 52. Manchester Coded Output of the AMC1306Ex
Figure 52. Manchester Coded Output of the AMC1306Ex