ZHCSO42B December 2015 – July 2021 LM53625-Q1 , LM53635-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Applications
- 9.2.1 General Application
- 9.2.2 Fixed 5-V Output for USB-Type Applications
- 9.2.3 Fixed 3.3-V Output
- 9.2.4 Adjustable Output
- 9.3 What to Do and What Not to Do
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.2.1.2.6 Maximum Ambient Temperature
As with any power conversion device, the LM53625/35-Q1 dissipates internal power while operating. The effect of this power dissipation is to raise the internal temperature of the converter above ambient. The internal die temperature (TJ) is a function of the ambient temperature, the power loss, and the effective thermal resistance, RθJA of the device and PCB combination. The maximum internal die temperature for the LM53625/35-Q1 is 150°C, thus establishing a limit on the maximum device power dissipation and therefore load current at high ambient temperatures. Equation 5 shows the relationships between the important parameters.
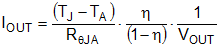
The device uses an advanced package technology that utilizes the pads/pins as heat spreading paths. As a result, the pads should be connected to large copper areas in order to dissipate the heat from the IC. All pins provide some heat relief capability but the PVINs, PGNDs and SW pins are of particular importance for proper heat dissipation. Utilization of all the board layers for heat dissipation using vias as heat pipes is recommended. The Layout Guideline section includes example that shows layout for proper heat management.