SLVA927A November 2017 – April 2019 LM25066A , LM25066I , LM5050-1 , LM5051 , LM5064 , LM5066 , LM5067 , LM5069 , LM66100 , LM74500-Q1 , LM74700-Q1 , TPL7407LA , TPS1H100-Q1 , TPS1HA08-Q1 , TPS2113A , TPS2115A , TPS22810 , TPS22915 , TPS22916 , TPS22918 , TPS22971 , TPS22990 , TPS23525 , TPS2412 , TPS24751 , TPS24770 , TPS25942A , TPS2595 , TPS2660 , TPS27S100 , TPS2H160-Q1 , TPS4H160-Q1 , ULN2003A
7 Low-Side Switches
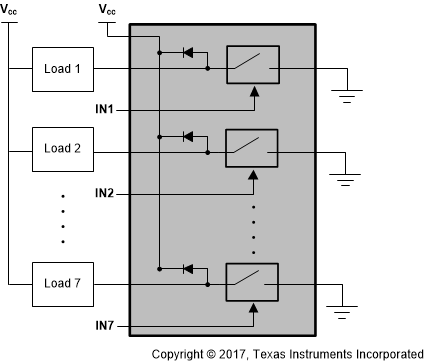 Figure 8. Low-Side Switch Block Diagram
Figure 8. Low-Side Switch Block Diagram Low-side switches are used to connect and disconnect ground from a load, unlike the rest of the power switch topologies. This configuration allows low-side switches to drive inductive loads; an internal flyback diode prevents inductive transients from damaging the circuit and components. Whenever the switch is opened, the inductive transients flow through the flyback diode and dissipate throughout the load. This makes these devices ideal for motors, solenoids, and relays.
Low-side switches consists of two designs: Darlington pair arrays and low-side MOSFET solutions. Darlington pair solutions can support higher voltage applications due to the higher voltage ratings of the integrated BJTs, while the MOSFET solutions have lower on-resistances and lower leakage currents. Most of the low-side switches contain seven channels, which can be tied in parallel to support higher current operation.
Table 8. Low-side Switch Examples
| DESCRIPTION | DEVICE | RECOMMENDED VOLTAGE RANGE | MAX CURRENT | NUMBER OF CHANNELS | PACKAGE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Darlington pair BJTs, higher voltage support | ULN2003A | 0 V to 50 V | 500 mA per channel | 7 | SOIC, SOP, and DIP Packages |
| Darlington pair BJTs, 8-channel support | ULN2803A | 0 V to 50 V | 500 mA per channel | 8 | SOIC |
| Low-side MOSFET solutions, low on-resistance and current leakage, power efficient | TPL7407LA | 0 V to 30 V | 600 mA per channel | 7 | SOIC or SOP |